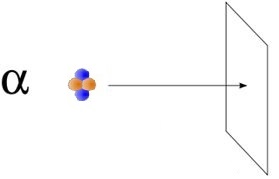
| As alpha radiation consists of positively charged He nuclei with energy in the order of several MeV it has a high ionization power,
and their penetration range in matter is rather low (1 cm in air, 1 μm in rock). The major radiation hazard from Alpha particles arises
from internal exposure, when alpha emitting nuclides are inhaled or directly ingested. As the penetration depth in human tissue is small,
the full energy of the alpha radiation will be absorbed by the cells. |
 |
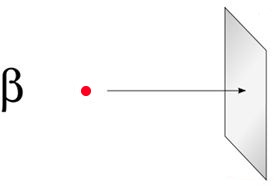
| Beta radiation has a continuous energy spectrum with a maximum energy specific for a given decay. The penetration range for 2 MeV beta
particles is about 8 m in air and 1 cm in water. Beta radiation has still a limited travel path in human tissues. In case of external exposure,
skin cells are the most affected in the body. |
 |
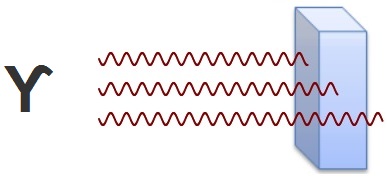
| Gamma radiation is electromagnetic radiation, and its ionization power is comparatively smaller. Its penetration in matter can reach several
cm in heavy materials. Gamma radiation is the most hazardous in the case of external exposure. |
 |


