2.8 Man-made sources of radiation
The first artificial radionuclide was "produced" by Jean Frederic and Irene Joliot Curie', in 1934.
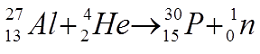
The main anthropogenic activities that have contributed to the dispersion of artificial radionuclides in the environment are:
- Weapon tests and use
- Accidents (e.g. Chernobyl, Fukushima)
- Nuclear Reactors (14C)
Most of the anthropogenic radionuclides are short-lived, but some have half-lives of many years. Among them, the more common are:
- 137Cs (30y)
- 90Sr (28.1y)
- 85Kr (10.73y)