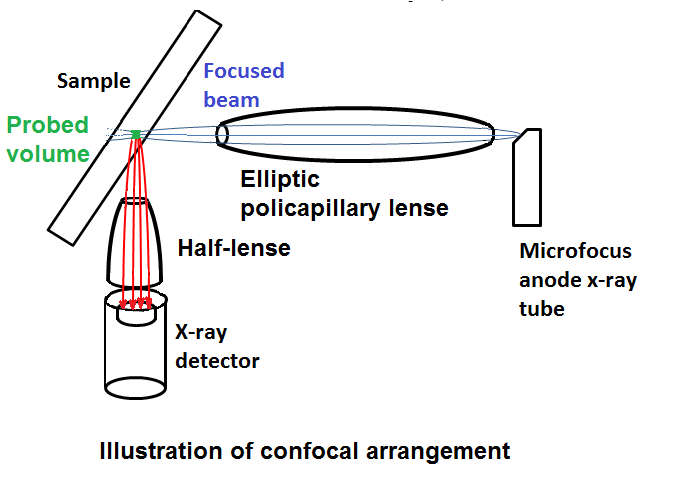
5.2.2 Confocal XRF
In Confocal-XRF spectrometers the excitation originating from a micro-focus x-ray tube is collected with a poli-capillary lens and focused onto the sample surface. Additionally a half-elliptical lens is placed in front of the detector, in a way that its collecting focus matches in position with the exit focus of the lens used for excitation.
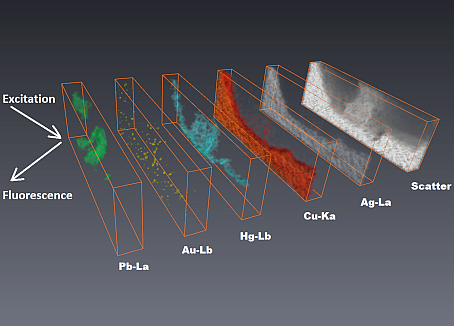
Sample is moved in X Y directions as to collect a plane map, and then displaced in depth (along Z axis) as to collect consecutive planes. The stacked maps can later be visualized in 3D representations depicting the distribution of the elements in the measured volume.
The typical resolution of the effectively probed voxel can be of about 20 – 20 – 20 μm. As the signal originating from deep layers undergoes attenuation in the upper layers, CXRF is mainly useful for the analysis of surface layers or for the analysis of light matrices. The fact that the paths travelled by the excitation and the fluorescent radiations are different makes difficult to account for attenuation corrections and the technique has been used mostly for qualitative representation of data.